What evolved first -- a dexterous hand or an agile foot?
Resolving a long-standing mystery in human evolution, new research from the RIKEN Brain Science Institute indicates that early hominids developed finger dexterity and tool use ability before the development of bipedal locomotion. Combining monkey and human behavior, brain imaging, and fossil evidence, a research team led by neurobiologist Dr. Atsushi Iriki and including Dr. Gen Suwa, an anthropologist from the University of Tokyo Museum, have overturned the common assumption that manual dexterity evolved after the development of bipedal locomotion freed hominid hands to use fingers for tool manipulation.
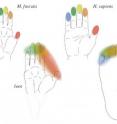
In a study published today in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, the researchers employed functional magnetic resonance imaging in humans and electrical recording from monkeys to locate the brain areas responsible for touch awareness in individual fingers and toes, called somatotopic maps. With these maps, the researchers confirmed previous studies showing that single digits in the hand and foot have discrete neural locations in both humans and monkeys.
However, the researchers found new evidence that monkey toes are combined into a single map, while human toes are also fused into a single map, but with the prominent exception of the big toe, which has its own map not seen in monkeys. These findings suggest that early hominids evolved dexterous fingers when they were still quadrupeds. Manual dexterity was not further expanded in monkeys, but humans gained fine finger control and a big toe to aid bipedal locomotion.
"In early quadruped hominids, finger control and tool use were feasible, while an independent adaptation involving the use of the big toe for functions like balance and walking occurred with bipedality," the authors explained.
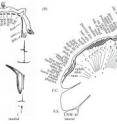
The brain study was supported by analysis of the well-preserved hand and feet bones of a 4.4 million year-old skeleton of the quadruped hominid Ardipithecus ramidus, a species with hand dexterity that preceded the human-monkey lineage split.
The findings suggest that the parallel evolution of two-legged locomotion and manual dexterity in hands and fingers in the human lineage were a consequence of adaptive pressures on ancestral quadrupeds for balance control by foot digits while retaining the critical capability for fine finger specialization.
"Evolution is not usually thought of as being accessible to study in the laboratory," stated Dr. Iriki, "but our new method of using comparative brain physiology to decipher ancestral traces of adaptation may allow us to re-examine Darwin's theories."
Source: RIKEN
Other sources
- Humans said to have evolved hand control while still quadrupedsfrom UPIMon, 7 Oct 2013, 21:30:18 UTC
- What evolved first—a dexterous hand or an agile foot?from PhysorgMon, 7 Oct 2013, 13:00:42 UTC
- What evolved first, a dexterous hand or an agile foot?from Science DailyMon, 7 Oct 2013, 1:30:15 UTC