Bed of needles
Related images
(click to enlarge)
A parasitic worm may hold the answer to keeping skin grafts firmly in place over wounds, according to a new study by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH). The study will be published in the April 16, 2013 issue of Nature Communications.
The research team, led by Jeffrey Karp, PhD, BWH Division of Biomedical Engineering, Department of Medicine, senior study author, invented a microneedle inspired by Pomphorhynchus laevis, a spiny-headed worm that lives in the intestines of its hosts, in this case fish. The worm securely attaches to the host's intestinal wall by penetrating, and then plumping up its elongated, cactus-like head into the intestinal tissue.
"Dr. Karp and his collaborators continue to look to nature to find new ways to solve real problems in medicine," said Scott Somers, PhD, National Institutes of Health's National Institute of General Medical Sciences, which partly supported the work. "Drawing on how parasitic worms attach to and feed on fish, they have designed a way to close surgical wounds that appears better than anything currently available for clinical use."
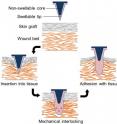
Inspired by the worm's swelling mechanism, Karp and his team created an adhesive patch that mechanically interlocks with tissue through swellable microneedle tips. The tips plump up via a water-based mechanism that is both quick and reversible.
"The adhesion strength of the tips of the microneedle is more than three times stronger than conventional surgical staples used for skin grafts fixation," said Seung Yun Yang, PhD, a BWH research fellow, and first study author.
Each cone-shaped needle is made of a stiff plastic non-swellable core and a tip that is rigid in its dry state, but swells upon contact with water. The bed of microneedles are able to effectively penetrate tissue with little force, as well as maintain continuous, seamless contact with tissue, and a high adhesion strength when the needles are in their swollen state.
"The unique design allows the needles to stick to soft tissues with minimal damage to the tissues. Moreover, when it comes time to remove the adhesive, compared to staples, there is less trauma inflicted to the tissue, blood and nerves, as well as a reduced risk of infection," said Karp.
The invention may one day be an alternative to the trauma- and infection-prone staples and sutures used in the operating room to secure skin grafts on patients with serious wounds as a result of burns, infection, cancer and other trauma.
The approach also offers the potential for delivery of therapeutics including proteins, and given its ability to attach strongly to wet tissues, the bio-inspired adhesive microneedles may be broadly applied during internal surgical procedures.
"I envision that this device will be very effective in treating patients, both by skin graft fixation, but also by delivery of active substances into the surface of the wound. These substances may be for example, antibiotics, growth-promoting compounds, or anti-inflammatory molecules," said Bohdan Pomahac, MD, director of both BWH Plastic Surgery Transplantation and the BWH Burn Center, as well as study author on the paper. "It's been a pleasure to collaborate with Dr. Karp, who is a visionary in science, to help provide the link to the microneedle adhesive's clinical applicability."
Source: Brigham and Women's Hospital
Other sources
- Inspired by spiny-headed worms, new microneedle adhesive 3x stronger than surgical staples in skin graft fixationfrom PhysorgTue, 16 Apr 2013, 15:31:05 UTC