Landsat 5 satellite sees Mississippi River floodwaters lingering
Related images
(click to enlarge)
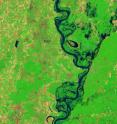
In a Landsat 5 satellite image captured June 11, 2011, flooding is still evident both east and west of the Mississippi River near Vicksburg, Miss. Standing water is most apparent, however, in the floodplain between the Yazoo and Mississippi rivers north of Vicksburg. On May 19, 2011, the Mississippi River reached a historic crest at Vicksburg. According to the Advanced Hydrological Prediction Service (AHPS) of the U.S. National Weather Service, the river reached 57.10 feet (17.40 meters) that day. By early June, flooding had receded considerably around Vicksburg, but water remained high.
On June 14, the AHPS reported that the Mississippi River reached 44.88 feet (13.68 meters) at Vicksburg. At that point, the river was in minor flood stage, and its level was forecast to continue falling through June 19.
The Landsat series of satellites is used by emergency managers to acquire a range of imagery, from floods to fires. Landsat has recently provided both images of the flooding of the Mississippi River and the fires raging in Arizona.
The Landsat Program is a series of Earth-observing satellite missions jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey. Landsat satellites have been consistently gathering data about our planet since 1972. They continue to improve and expand this unparalleled record of Earth's changing landscapes, for the benefit of all. The next Landsat satellite is scheduled to launch in December 2012.
Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center
Other sources
- Landsat 5 satellite sees Mississippi River floodwaters lingeringfrom Science DailyFri, 17 Jun 2011, 2:30:18 UTC
- Landsat 5 satellite sees Mississippi River floodwaters lingeringfrom PhysorgThu, 16 Jun 2011, 21:30:40 UTC