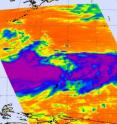
Tropical Storm Muifa appears huge on NASA infrared imagery
The width of an image from the AIRS instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite is about 1700 km (1056 miles), and the clouds and thunderstorms associate with Tropical Storm Muifa take up that entire distance on today's imagery. Tropical Storm Muifa is spinning through the western North Pacific Ocean today and has grown in size. When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the storm on July 29, 2011 at 04:17 UTC (12:17 a.m. EDT) it measured the temperatures in the cloud tops. Those cloud top temperatures especially in the east and western sides of the tropical storm were colder than -62 Fahrenheit/-52 Celsius, indicating strong storms with heavy rainfall. Fortunately, much of that heavy rainfall was over open ocean.
Today's image shows that the center of the storm appears almost cloud free and there was strong convection (rapidly rising air that form thunderstorms) and strong thunderstorms on the east, south and western sides of the storm. Convection on the north side of the tropical storm is still being suppressed by the same weather system that affected it yesterday.
At 1500 UTC (10 a.m. EDT) on July 29, Tropical Storm Muifa had maximum sustained winds near 55 knots (63 mph/101 kmh) and was moving north at 6 knots (7 mph). It was located about 815 nautical miles south-southeast of Kadena Air Base near 14.1 North and 133.9 East.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center forecasters expect Muifa to strengthen over the next couple of days as it moves north across the Pacific.
Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center
Articles on the same topic
- Tropical Storm Don analyzed in 3 NASA satellite imagesFri, 29 Jul 2011, 20:35:07 UTC
- NASA identifies the areas of Tropical Storm Muifa's strength Thu, 28 Jul 2011, 19:14:57 UTC
- NASA eyes Tropical Storm Nock-Ten's heavy rains for Hainan Island and VietnamThu, 28 Jul 2011, 19:14:49 UTC
- GOES-13 satellite movie shows formation of Tropical Storm DonThu, 28 Jul 2011, 14:36:02 UTC
- Tropical Depression 11W moving past Yap and GuamWed, 27 Jul 2011, 18:36:23 UTC
- NASA measures heavy rain in Tropical Storm Nock-Ten over PhilippinesWed, 27 Jul 2011, 18:36:13 UTC
- NASA sees Tropical Storm Nock-ten knocking the PhilippinesWed, 27 Jul 2011, 15:05:46 UTC
- NASA sees dramatic temperatures around Tropical Depression 11WWed, 27 Jul 2011, 15:05:35 UTC
- Tropical Depression 10W bringing rain to the PhilippinesWed, 27 Jul 2011, 15:05:23 UTC
Other sources
- Tropical Storm Don analyzed in 3 NASA satellite imagesfrom PhysorgSat, 30 Jul 2011, 8:30:30 UTC
- NASA identifies the areas of Tropical Storm Muifa's strengthfrom PhysorgThu, 28 Jul 2011, 19:10:42 UTC
- GOES-13 satellite movie shows formation of Tropical Storm Donfrom PhysorgThu, 28 Jul 2011, 15:30:45 UTC
- NASA sees Tropical Storm Nock-ten knocking the Philippinesfrom PhysorgWed, 27 Jul 2011, 15:02:23 UTC
- NASA sees dramatic temperatures around Tropical Depression 11Wfrom PhysorgWed, 27 Jul 2011, 15:02:18 UTC
- Tropical Depression 10W bringing rain to the Philippinesfrom PhysorgMon, 25 Jul 2011, 21:00:40 UTC