Study finds that overweight people really are big-boned
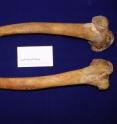
One of the blind spots in forensic science, particularly in identifying unknown remains, is the inability of experts to determine how much an individual weighed based on his or her skeleton. New research from North Carolina State University moves us closer to solving this problem by giving forensic experts valuable insight into what the shape of the femur can tell us about the weight of an individual. "This research allows us to determine whether an individual was overweight based solely on the characteristics of a skeleton's femur, or thigh bone," says Dr. Ann Ross, an associate professor of anthropology at NC State and co-author of a paper describing the research. However, Ross notes, this research does not give us the ability to provide an individual's exact weight based on skeletal remains.
Researchers found that the heavier an individual was, the wider the shaft of that person's femur. The researchers hypothesize that the femur of an overweight person is more robust because it bears more weight, but also because overweight individuals move and walk differently to compensate for their greater mass.
The researchers evaluated the femur bones of 121 white men for the study. They used the bones of white men exclusively in order to eliminate any variation that could be attributed to race or gender.
The lead author of the paper, "The Effect of Weight on the Femur: A Cross-Sectional Analysis," is Gina Agostini, who did the work while a graduate student at NC State. The paper is published in the March issue of the Journal of Forensic Sciences.
Source: North Carolina State University
Other sources
- Study: Bones can give clue to weightfrom UPITue, 22 Mar 2011, 22:00:30 UTC
- Forensics: Overweight people really are big-bonedfrom Science DailyTue, 22 Mar 2011, 16:30:56 UTC
- Overweight People Really Are Big-Bonedfrom Science BlogTue, 22 Mar 2011, 15:00:11 UTC
- Study finds that overweight people really are big-bonedfrom PhysorgTue, 22 Mar 2011, 14:00:29 UTC